In this post
Crop plants are those grown by farmers or gardeners as a source of food. Glasshouses and polythene tunnels can be used to increase the yield of certain crops. Glasshouses (or greenhouses) are made of glass supported in a metal framework, as shown in the diagram here.

Polythene tunnels are made of polythene supported in a tunnel shaped framework, as shown in the diagram below.

Both structures are designed in such a way as to increase the crop yield by providing the ideal conditions needed for maximum photosynthesis and plant growth to occur.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants take in the light energy provided by the Sun and use it to combine water taken in by the roots and carbon dioxide taken in from the air, to produce food and oxygen as shown by the equation:
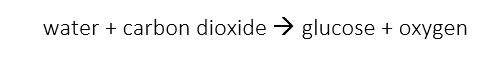
The ideal conditions for a good rate of photosynthesis and high level of plant growth include high amounts of light, high temperature and a plentiful supply of carbon dioxide gas.
Glasshouses and polythene tunnels are transparent to maximise the amount of sunlight which can get through to the crop plants inside. Artificial lights can also be used inside both structures so that the plants can also photosynthesise when the natural light outside is at too low a level.
The glasshouses and polythene tunnels also trap the heat from the Sun inside, meaning that the plants and their enzymes are kept at a constant temperature.
The temperature inside glasshouses and polythene tunnels can also be increased by burning fossil fuels such as oil through oil burners. This increase in temperature causes an increase in the rate of photosynthesis and therefore an increase in the rate of crop growth which occurs.

Using oil burners also produces the gas carbon dioxide which plants take in during photosynthesis. The more fuel is burned, the more the levels of carbon dioxide increase. As a result, the rate of photosynthesis and crop yield increases.
A high humidity is also maintained inside glasshouses and polythene tunnels. The amount of transpiration occurring decreases, reducing the amount of water lost by the plants to the atmosphere. This maximises the amount of water available for plants to use in photosynthesis and therefore increases the rate of photosynthesis which occurs.
The use of fertilisers, especially those containing nitrogen, phosphates and potassium (NPK fertilisers), also increases crop yield. Nitrogen is needed to produce plant proteins for growth. Phosphates are needed for DNA and cell membranes, and potassium is needed for the maintenance of cell membranes. Fertilisers are spread onto the soil and plants absorb the nutrients from the soil through their roots. These nutrients allow the plants to grow bigger and faster therefore increasing the crop yield.
Glasshouses and polythene tunnels also protect the crops from the weather. This means that less crop plants will be lost due to poor weather conditions and crops can be continually grown throughout the year regardless of the season. Glasshouses and polythene tunnels also provide shelter and protection from disease and pests, again reducing the number of crop plants lost and maximising crop yield.
Pests are any organism which will destroy the crops. The main group of pests which destroy crop plants are insects, including aphids, crickets, beetles and moths. They tend to eat the leaves and stems of a plant which will prevent the plant from photosynthesising, leading to its death. It is essential that crops are protected from pests to maximise crop yield and prevent the plants being destroyed.
There are two main types of pest control used by farmers and gardeners. The first type is a group of chemicals known as pesticides. Pesticides are chemicals which kill the pest but do not harm the crop. The advantages of using pesticides include that they are:
- Easy to source and buy
- Fast and easy to apply – usually by spraying them over the crop plants
- Very effective at killing the pests whilst not harming the plants
Key term
Pesticides – a group of chemicals used to kill pests, but which do not harm the crop.
The disadvantages of pesticides are that:
- They are toxic so could harm or kill living organisms other than the pests or could kill other plants
- They can accumulate in the food chain causing harm for animals in the higher trophic levels
- The pests may develop a resistance through mutations meaning that to be effective the pesticides must be applied at higher concentrations or alternative pesticides must be found
- Killing the pests can result in a decrease in biodiversity in ecosystems
- Pesticides can leach into the soil and be washed out into rivers or lakes causing eutrophication
The second type is known as biological control which makes use of living organisms which will kill the pest but will not eat the crop plant. An example of biological control in action is the use of ladybirds to kill aphids. Aphids will eat and destroy crop plants. Ladybirds will eat the aphids on the crop but will not eat the plant itself. The advantages of using biological control include:
- No toxic chemicals are involved which may pose a threat to humans or wildlife
- It is cheaper
The disadvantages of using biological control include:
- It is not as effective as using pesticides
- It can be difficult to control the number of predator organisms
- It can be difficult to find a suitable predator to match the pest
- It takes longer for the pests to be eaten so the plant may be damaged more than it would if a pesticide was used
- The predators may enter the ecosystem surrounding the plant therefore affecting the biodiversity of the ecosystem
Microorganisms
Microorganisms are living organisms which are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Yeast and bacteria are two examples of microorganisms which are used in the production of food. Yeast is commonly used in the production of bread and beer through the process of fermentation. Fermentation is a chemical process where a substance is broken down by yeast to release energy.
Yeast can undergo both aerobic (using oxygen) and anaerobic (using no oxygen) respiration. In the production of bread, the yeast breaks down the glucose into carbon dioxide and water in the process of aerobic respiration as shown by the following equation:
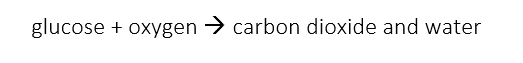
The bubbles of carbon dioxide gas produced cause the bread dough to rise.
Bacteria is used in the production of yoghurt. The bacterium used to produce yoghurt from milk is named Lactobacillus. The whole process by which the milk is turned into yoghurt is known as fermentation. As the bacterium being used for this process is specifically Lactobacillus, it is essential that all the equipment being used is sterilised to remove any other bacteria or unwanted microorganisms which would contaminate the milk.
The milk itself is pasteurised to remove any microorganisms in the milk. This is done by heating the milk to a temperature of 72oC for 15 seconds. The milk is then cooled, and the Lactobacillus is added. The bacteria and milk mixture is incubated at 40 oC in a fermenter where the Lactobacillus ferments the lactose in the milk into lactic acid. This bacterium uses the sugar lactose present in the milk to produce lactic acid through anaerobic respiration. The lactic acid causes the proteins in the milk to clump together. The milk becomes thicker and more solid, creating yoghurt.
Microorganisms such as bacteria and yeast are used in chemical reactions to produce a wide range of products including food, medicines, fuels and enzymes. These reactions are performed inside industrial fermenters as the environmental conditions can be carefully monitored and controlled according to the type of microorganism being used and the reaction taking place.
Suitable conditions needed inside the fermenter to allow the growth of microorganisms include:
- Aseptic procedures should be used to remove any other unwanted microorganisms from the fermenter which would contaminate the reaction mixture. This may involve sterilisation using heat or steam.
- Addition of the nutrients needed to allow the microorganism to grow.
- Optimum temperature and pH to make sure that the enzymes are acting at their maximum rate and are not denatured.
- Oxygen gas is essential to allow the microorganisms to respire aerobically and is provided via an inlet pipe into the fermenter.
- The carbon dioxide produced by the respiration is removed constantly.
- The mixture must be constantly agitated (stirred) using blades controlled by a motor. This constant agitation makes sure that the components of the reaction mixture are constantly in contact and ensures that the temperature and concentration of the reaction mixture is the same throughout
Fish farming
Fish are a good source of protein in the human diet. Large numbers of fish are needed. To avoid the need for mass fishing from the sea and other natural habitats, fish farms are often used to supply the fish. In fish farms large numbers of fish are bred to meet the high demands for protein.

The methods used to farm the large numbers of fish needed must be carefully considered to make sure that the maximum numbers of fish are produced in the shortest amount of time possible.
Fish produce waste products such as faeces which can accumulate in the water. The quality of the water in the tanks that the fish are kept in must be regularly monitored to make sure that the fish are not being exposed to high levels of waste, chemicals or anything else that could harm the fish or cause disease. The water is filtered to remove large pieces of debris. The water in the fish tanks and the tank itself is cleaned and sterilised regularly to remove waste and harmful bacteria and prevent the spread of disease throughout the fish population. The level of oxygen in the water is controlled to make sure that it is high enough for the respiration of the fish.
- Intraspecific predation – this type of predation occurs when members of the same species compete with and feed on each other. Within the same species, the larger fish may eat the smaller fish. To avoid this predation occurring in the fish farms, the fish are kept in large tanks and are given adequate supplies of food to avoid overcrowding and competition for food. The fish are also separated by age, size and gender.
- Interspecific predation – this type of predation occurs when members of different fish species compete with and feed on each other. To avoid this predation occurring in the fish farms, the fish are separated by species. One species of fish is kept in each separate tank and the tanks are covered with mesh or netting to ensure that the fish are not able to leap into other tanks. The fish are also supplied with an adequate amount of food to prevent competition and are separated by gender to allow the control of the breeding programme.
- Control of disease – the number of fish kept in each tank is minimised where possible to limit the number of fish affected by any disease which can be passed between them. Pesticides and antibiotics may also be added to the water to prevent microorganisms reproducing and spreading disease. However, this can be a source of concern as the pesticides and antibiotics may be ingested by the fish and then passed to humans through the food chain when they eat the fish.
- Control of the quality and frequency of feeding – to avoid overeating or competition between the fish for food they are fed small amounts of food on a very regular basis. The fish are often deliberately fed with protein-rich food to promote their growth. Some fish farms will also add growth hormones to the water to speed up the growth of the fish.
- Selective breeding – fish farmers want to produce large numbers of fish which are as large and as healthy as possible. To achieve this, the farmers use selective breeding where only the fish with these desired characteristics are chosen to breed. The largest and most healthy fish will be allowed to breed whereas the smaller or unhealthy fish are prevented from breeding by separating them by gender into different tanks. The continued use of selective breeding means that over time the whole population of fish should be larger and healthier, and the smaller and less healthy fish population will decrease and die out completely as they are not reproducing to pass on their genes.


