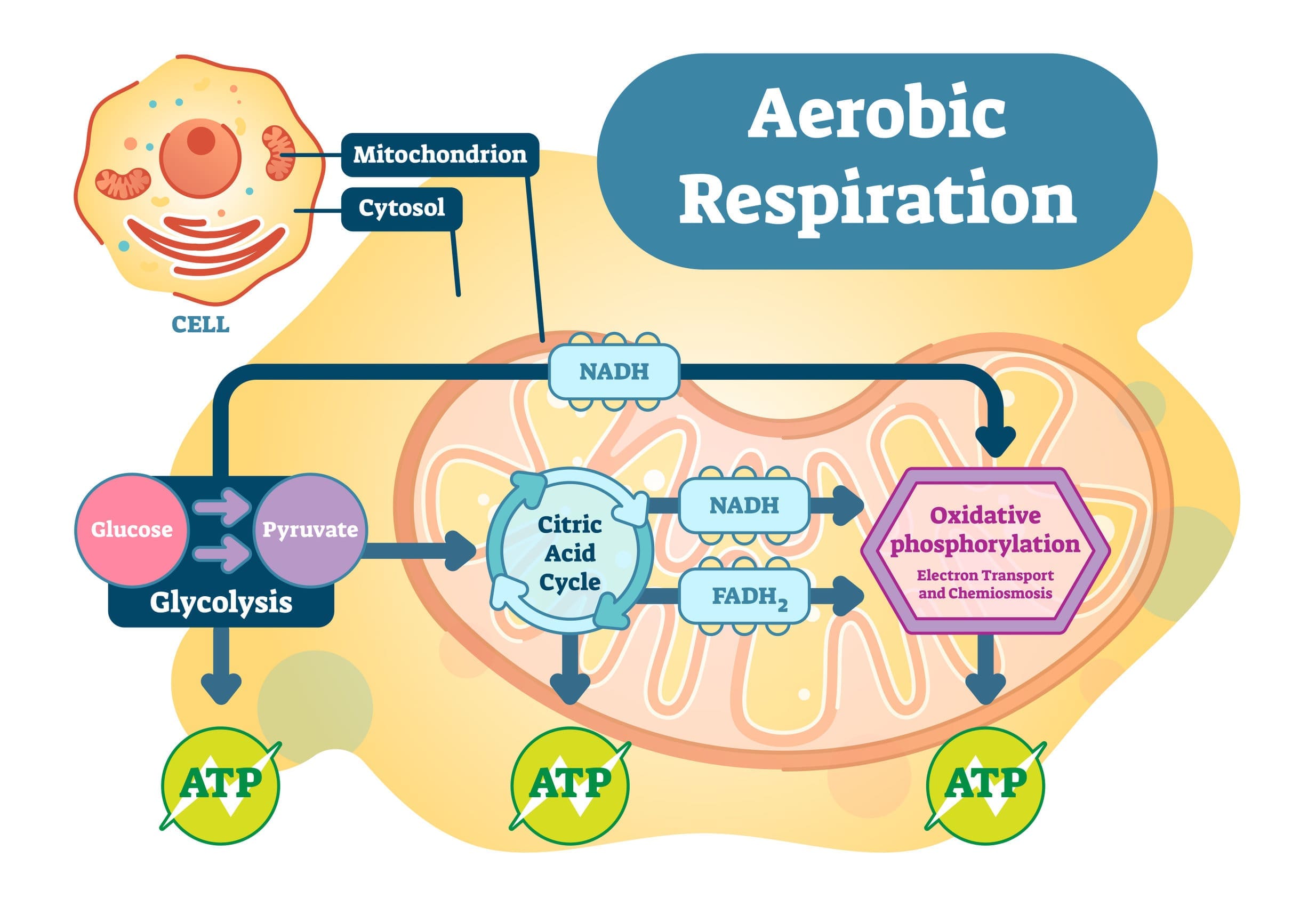
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen. Aerobic processes include the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain. However, glycolysis is an anaerobic process, meaning that it does not require any oxygen. When oxygen is not around, instead of the products of glycolysis going into the Krebs cycle, they will undergo a process known as fermentation. Anaerobic respiration does not produce as much energy as aerobic respiration because glucose is not completely broken down during this process.
Fermentation is when plants and microorganisms chemically break down food substances into simpler substances which will be useful to them. When this happens, carbon dioxide is also formed and then released as a waste product. Anaerobic respiration sometimes occurs in plants when there is little oxygen present, for example in the roots of plants in waterlogged soils.
However, the most common instance of fermentation involves yeasts (a microorganism), more specifically Saccharomyces cerevisiae which is a single-celled fungus. When this yeast undergoes fermentation due to the absence of oxygen, it converts glucose into alcohol. This is known as alcohol fermentation. For the exam, you will also need to know the word equations and the chemical equations for anaerobic respiration:
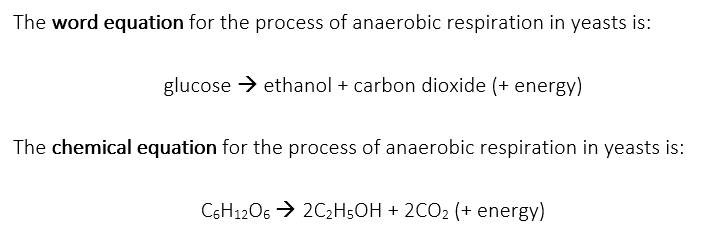
In humans and animals, muscles do not directly produce alcohol when oxygen is not around but instead produce lactic acid. The production and build-up of lactic acid due to a lack of oxygen is why our muscles hurt after vigorous exercise as oxygen-starved muscle cells produce lactic acid. This is known as lactic acid fermentation. It is also useful to know the word and chemical equations for anaerobic respiration occurring in animal organisms:
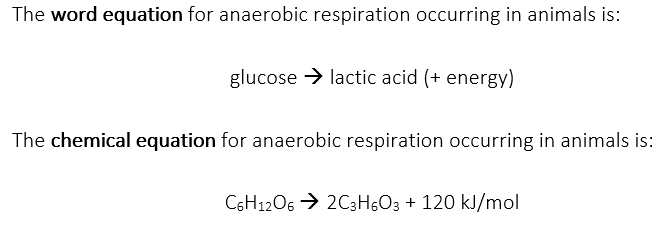
In the above equations, energy is shown in brackets because it is not a chemical substance.