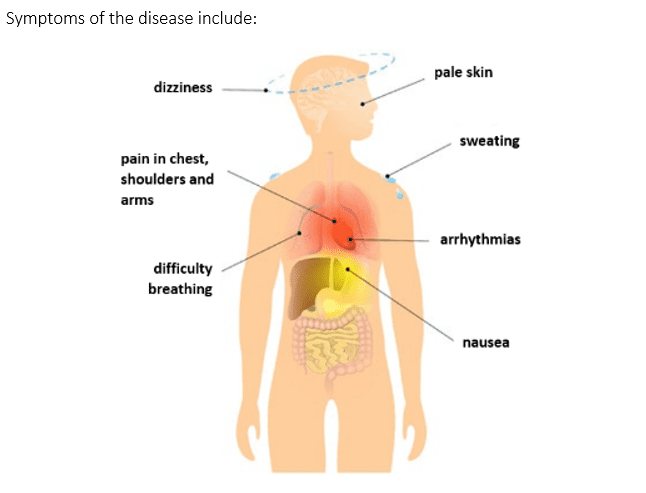
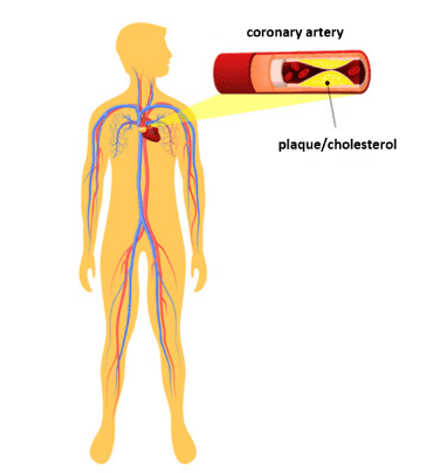
Coronary heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease, refers to the build-up of fatty substances in the walls of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries are among the narrowest arteries in the body and so they can easily be blocked. When fatty substances build up in the walls of coronary arteries, it can cut off the blood supply to an area of cardiac muscle, affecting its ability to contract and ultimately increasing the risk of a heart attack.
There are a number of factors that increase the risk of coronary heart disease. These are:
- Heredity – some people can inherit a tendency of developing coronary heart disease.
- Diet – eating more saturated fat can increase a person’s level of cholesterol.
- High blood pressure – puts the heart under more strain.
- Stress – raises high blood pressure.
- Smoking – makes blood clots more likely to form and raises a person’s blood pressure.
- Lack of exercise – regular exercise helps to strengthen the heart and reduce a person’s blood pressure.