In this post
All living organisms get the energy they require from a process known as cellular respiration.
As we can see from the word and chemical equations, the processes of photosynthesis and respiration are opposites:
Photosynthesis
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[carbon dioxide + water \to glucose + oxygen\]](https://b3801007.smushcdn.com/3801007/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0335a84aa75f2eb09fab4d8edd568771_l3.png?lossy=2&strip=1&webp=1)
or:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[6CO_2+6H_2O \to C_6H_{12} O_6 + 6O_2\]](https://b3801007.smushcdn.com/3801007/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-79ddb29e88977f31e90e05720721782d_l3.png?lossy=2&strip=1&webp=1)
Respiration
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[glucose + oxygen \to carbon dioxide + water (+ energy)\]](https://b3801007.smushcdn.com/3801007/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-fa577ad705b1b8577d26b8877bf758d5_l3.png?lossy=2&strip=1&webp=1)
or:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[C_6H_{12}O_6+6O_2 \to 6CO_2 + 6H_2O(+energy)\]](https://b3801007.smushcdn.com/3801007/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-da10695d55e9bbf863affe92e90cbd89_l3.png?lossy=2&strip=1&webp=1)
Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and produces oxygen, whereas respiration uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide.
Another difference that separates these two processes is that photosynthesis does not continue during the night but respiration continues during the day and night in flowering plants. This causes a build-up of carbon dioxide in the air surrounding the plant during the night:
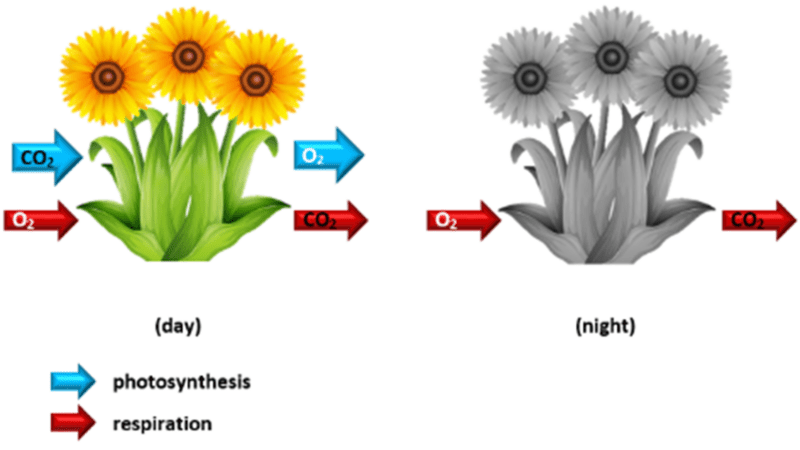
| Time of day | Photosynthesis | Respiration |
| Day | Active | Active |
| Night | None | Active |



