On average, the heart beats approximately 70 times per minute. However, this rate can change according to different circumstances, for example during exercise, due to the secretion of adrenaline, and when we sleep.
During exercise, the muscles are required to release more energy. This means they need an increased supply of oxygen for aerobic respiration – if the muscles do not receive enough oxygen they will start to respire anaerobically, producing a build-up of lactic acid. In order to deliver more oxygen to these muscles, the heart rate (the beats per minute) and the stroke volume (the volume of blood pumped with each beat) increases.
A hormone known as adrenaline is secreted from the adrenal glands when we undergo stress (are angry or afraid). The secretion of adrenaline causes heart rate to increase, supplying extra blood to the muscles and allowing them to respire aerobically. This is known as the ‘fight or flight’ response, allowing us to fight or run away from a stressful situation. We will discuss the secretion of hormones in much more detail in a later topic.
Changes to the heart rate also occur when we sleep as our organs work much more slowly. Heart rate decreases because organs do not require as much oxygen because they are not using up that much energy.
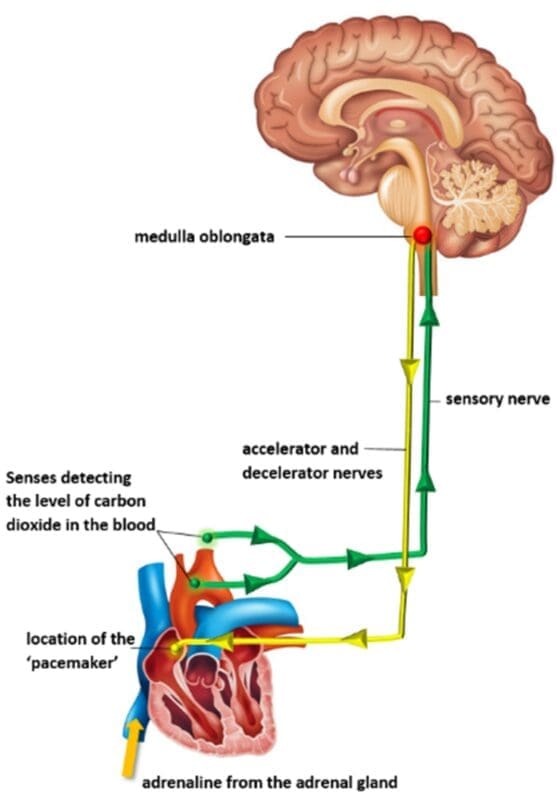
Nerve impulses located in the part of the brain known as the medulla oblongata control these changes in heart rate. During exercise, muscles produce more carbon dioxide due to an increase in their aerobic respiration rate and senses in the aorta and the carotid artery (the artery leading to the head) detect this increase and send nerve impulses to the medulla oblongata via sensory nerves. The medulla oblongata responds by sending nerve impulses back to the heart via the accelerator nerve telling it to increase its heart rate. When carbon dioxide levels in the blood return to normal, the medulla oblongata will receive fewer impulses and respond by sending nerve impulses along the decelerator nerves, slowing the heart rate.
The cardiac centre is the name given to the precise region in the medulla oblongata that controls heart functions, and pacemaker refers to the site of the heart which generates the energy that pumps the heart.