In this post
Motivation in a business is something that should never be overlooked. A company could have a great product, fantastic marketing and efficient operating methods, but, if the staff they employ are not motivated to do their jobs, this will all come to nothing.
Motivation is defined as the desire to achieve a goal. In order to inspire this motivation, companies can use a variety of different motivational techniques. Some people will be naturally motivated and need little encouragement, whereas others may need a lot of encouragement at work, so it is very important that a business can tailor its approach to each individual.
The importance of motivation
Businesses that have a highly motivated workforce will work to higher levels. Each individual will perform better and profits are likely to be higher. Some of the main benefits of a highly motivated workforce will include:
- Higher production rates – staff that are highly motivated will work harder. They will take more pride in their work and have a higher level of output than those that are not motivated. This means the business gets more from each person and will therefore need less staff to perform to the highest levels
- Lower staff turnover and absenteeism – motivated employees will be very dedicated to their job. This means they will stay for longer and be much less likely to take time off sick. This means the business can save money in recruitment costs and keep the same staff for long periods of time in order to uphold high standards
- More innovation – in jobs that rely on thought processes and being able to come up with solutions, motivation is even more essential. Well-motivated workers will think about things in a different way and be able to tackle situations in a strategic manner
- Better working environments – a team that is highly motivated will be able to work seamlessly with each other. This will build a pleasant atmosphere in the workplace, as each person supports their colleagues. Over time a company will see the benefits of this through better customer support, fewer disagreements, lower staff turnover and reduced stress
- Attracting new employees – having an already motivated team will help a business to attract new members. People are much more likely to want to be part of a business that supports individuals and motivates each employee, so the best candidates can be attracted for new job roles
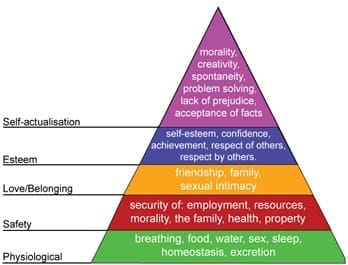
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Many experts have tried over the years to develop theories that help to motivate people in the workplace. One of the most famous of these was created by Abraham Maslow and shows a hierarchy of needs that people must work towards. These include:
Physiological needs
This is the most basic level of the hierarchy and must be achieved first before a person can move on to the next. These types of needs include oxygen, water, food, sleep and warmth and are things that humans simply cannot survive without. Once these needs are met, individuals can go on to seeking safety.
This is the first need within a job role. An employee will need a job to earn money and to be able to support their most basic needs.
Safety needs
This level is concerned with security, stability and protection in everyday situations. That is to say that at this level, people need to exist in a predictable and orderly world that they feel is mostly within their control. Many mental health issues are believed to be founded in individuals feeling as though they are not empowered over their own lives, i.e. they have no control over them.
This section of Maslow’s hierarchy relates to job security. People will need to be able to feel secure in their position and must be able to control what they do within their job to a certain extent.
Belongingness and love
In order not to feel isolated and anxious, the needs at this level are companionship, affection, intimacy and love. This can include things like being a member of a social group, having a stable, reliable set of friends and being in a committed relationship, where you are able to love and be loved. When people do not feel loved and cared for, they can feel very vulnerable, which can lead to mental health issues.
This part of the hierarchy relates to being accepted into a new job role. People will need to work with like-minded individuals and feel that they are part of the company as a whole in order to build a sense of responsibility and belonging.
Self-esteem needs
To satisfy these needs, people need to achieve and become competent and be recognised as such. Also at this level, intellectual needs must be met, and so it is paramount that people have understanding and knowledge. Self-respect is important to gain at this level because it connects with all of the aspects required to move on to the final level in the hierarchy. People who have mental health issues often have deep-rooted low self-esteem and this has been identified by much research as a potential cause of anxiety and depression related conditions.
Motivation links very strongly to self-esteem needs. To get to this stage, people will need to be recognised for the work that they put in and feel that this is appreciated by those around them in the company.
Self-actualisation needs
People at this level should also strive for continuous improvement to ensure maintenance of their current status, because according to Maslow, by this point, all of the individual’s needs have been met.
When people reach the very top of their careers they will seek to have their self-actualisation needs fulfilled. It is quite rare that people ever get to this stage as most people will always have some other need that is not yet completely fulfilled. This final stage relates to a person feeling that their life’s work has been worthwhile and being satisfied with all aspects of their career.
Motivation methods
Businesses use a number of different techniques to motivate their employees. These techniques are often split down into two different categories: financial and non-financial. As the name suggests, financial rewards will repay someone for their hard work through giving them more money and non-financial methods will focus on giving other incentives to work hard that do not necessarily earn an employee more.
Financial rewards
Most people go to work to earn money. They need money to pay bills and buy things that allow them to live and enjoy their life. This means that a business can use payment systems to motivate staff as they will want to work harder so that they are financially secure. Financial rewards can be structured in several ways:
- Time rates – a time rate is very common in any business. It rewards people for the time that they spend at work and the number of hours they put into their job. The hours that a person works will earn them a set rate and any additional hours above an agreed amount may result in overtime being paid. This is where the company will pay a higher rate of pay for additional hours. For example, a person that earns £10 per hour may get overtime at a rate of 1.5 when they work later than 5:00pm. This means that for every hour they work after 5:00pm they will earn 1.5 times their pay which is equal to £15 per hour.
- Piece rates – a piece rate is an amount that is given to an employee based on their productivity. Usually this type of pay is used in manufacturing or when collecting produce from farms, and motivates people to work at a good rate in order to get paid more money. Workers who are lazy and unproductive will get paid less than those who work hard and have a higher output. This will help a business to get more from their employees and can be used to calculate the amount that the business makes for every product created.

- Commission – this is quite similar to being paid a piece rate and is based on rewarding outcomes. People working in sales are typically paid a commission as they will earn a percentage of the amount they bring into the company. If no sales are made, then a business has not made any money – something that is reflected in an employee’s wage. In reality though, commission payments are very rarely done like this. Salespeople often get a basic wage and then have this topped up by commission payments when sales are made
- Bonuses – when specific targets are met in a business, bonus payments may be given to employees. These payments will be in addition to the usual pay rates and will motivate employees to meet targets that are set
- Performance-related pay – this type of pay is used to motivate people by offering more money if managers are happy with progress. Although basing pay on sales commission is a form of performance-related pay, the term itself can relate to a wider range of areas of a job role. The progress of an individual, targets that are met and training that has been undertaken, may all impact upon the amount of money that is paid to an employee
- Profit sharing – usually used for staff members that are quite high in the company hierarchy, profit sharing will encourage people to take ownership over the business and work harder. This method relies on workers being rewarded financially when the business succeeds. If the business makes money, so do the employees
Non-financial methods
Non-financial methods of motivation are used for a lot of different reasons. Although everybody is motivated by money to a certain degree (in that money is needed to survive), some people will simply not react well to incentives that are purely financial. For some job roles, financial benefits lose their effectiveness as the people in them will value other things higher than money.
Non-financial benefits are commonly known as ‘fringe benefits’ and will be the different things that a company can offer on top of a wage. These benefits may include:
- Use of the company’s facilities such as a gym or canteen
- Company vehicles
- Subsidizeded accommodation or food
- Pension contributions
- Childcare vouchers
- Health insurance
- Awards and recognition of achievement
Although many of these fringe benefits may cost a business money, the amount is unlikely to outweigh the benefit. For example, if an employee receives £500 worth of fringe benefits in their job they will save this money, but the business, since they are paying for these benefits in bulk, may only pay out £250 per person to offer these rewards. This means that an employee can benefit from incentives in their role that are worth more money than a business would be prepared to give through financial methods of motivation.



