In this post
Metallic elements are found on the left side and middle of the periodic table.
A piece of a metal is made up of a metallic structure known as a metallic lattice which is held together through metallic bonding.
We know that metals always want to lose electrons from their outer shell to achieve stability. A metal only contains metal atoms. As the metal atoms cannot transfer their outer shell electrons to other metal atoms, they donate them instead to a ‘sea of delocalised electrons’. Delocalised electrons are those electrons which have not been used in bonding and are free to move throughout the whole structure rather than staying local to one atom. Once the atoms have delocalised their outer electrons they become positively charged ions.
All of the metal atoms in a sample of metal will delocalise their electrons to become positive ions. A metallic lattice is made up of a large number of positive metal ions and negative delocalised electrons. You must known how to represent a metallic lattice using a 2-D diagram such as the one below:
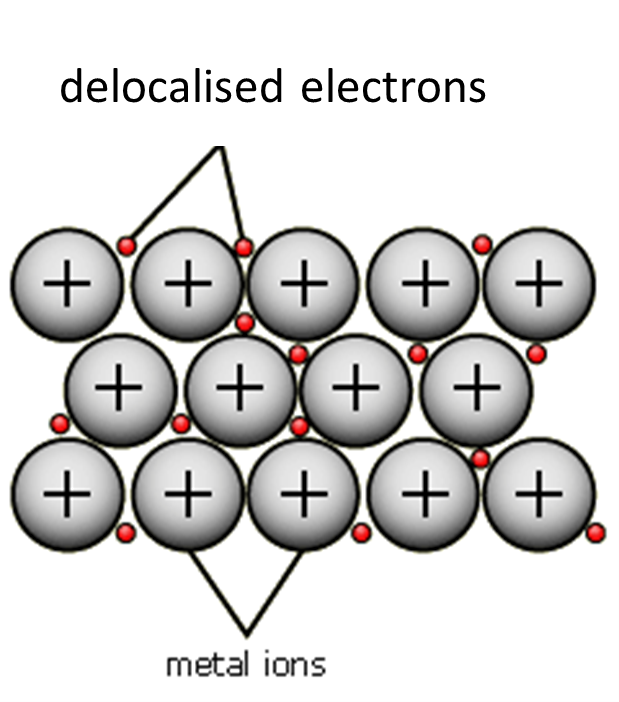
There is an electrostatic force of attraction between a positively charged metal ion and a negatively charged delocalised electron. This force of attraction is known as a metallic bond. The strength of the metallic bonds throughout the structure keeps the metallic lattice together.
Properties of metallic structures
The properties of metals can be explained using metallic bonding.
- Metals have high melting and boiling points. The metallic bonds found throughout the whole metallic lattice structure are very strong. Melting the metal would require the breaking of these bonds which would take lots of energy due to their strength and number
- Metals are hard, strong and have a high density. The metal ions in the metallic lattice are closely packed together with only very small gaps between them. This, along with the strength of the metallic bonds, makes the structure very hard, dense and strong and makes them suitable for a range of uses such as making bridges and vehicles
- Metals are good conductors of electricity. For example, copper is used in electrical wiring as it is a good conductor of electricity. Metals are able to conduct electricity due to the delocalised electrons which are free to move and carry charge throughout the metallic lattice structure
- Metals are malleable and ductile. Malleable means that the metal can be moulded into a variety of different shapes. Ductile means that the metal can be stretched out into thin wires without breaking
The metal ions in a metallic lattice are arranged in layers which are able to slide and move over each other. If heat is applied to a metallic lattice, the forces of attrraction holding the layers of ions in place are overcome and the layers can slide over each other. By applying force to a metallic lattice, we can also move the layers of atoms over each other into new positions.
This means that we can use a combination of heat and force to force the layers of ions to move and change the shape of the metal. This is very useful in manufacturing as these metallic structures can be changed into whatever shape is needed and they will still be strong.
Alloys
Alloys are a mixture of two or more different metals and are stronger than pure metals. When two different metals are mixed, the regular metallic lattice structure is disrupted because the metal atoms are all different sizes. This difference in size of the metal atoms changes the regular arrangement of the layers and prevents them from sliding over each other. As the layers cannot slide over each other, the structure becomes stronger and less malleable and ductile




