In this post
Time relating to distance and speed
Time is something which is necessary to work out a relation between distance and speed. If we said that someone travelled 5km, we could not work out their average speed without first knowing the amount of time it took them. Therefore, the idea of time is very important in working out these relations. We will, however, begin with some basics on time, converting the units used and calculations with different times.
Time is generally given in minutes and seconds and the conversion between different measurements of time is fairly simple as there are the same amount of seconds in a minute as there are minutes to an hour.
Obviously, since there are 60 seconds in a minute and 60 minutes in an hour, we use this to convert between them. So, to convert hours to minutes we must multiply by 60 and to change minutes to seconds we must again multiply by 60. Then to go from seconds to minutes we divide by 60 and from minutes to hours we divide by 60 again.
Example
Convert the following:
a) 420 seconds into minutes
b) 90 minutes into hours
c) 0.2 hours into seconds
a) Here we need to divide 420 by 60 as stated above when converting seconds to minutes. So we get an answer of ![]() minutes
minutes
b) With this we need to again divide by 60. So we get 90 divided by 60 which gives an answer of 1.5 hours
c) Finally, we must first convert 0.2 hours to minutes by multiplying by 60 to get 12 minutes. And then multiply again by 60 to get the answer in seconds; this gives 720 seconds
Adding and subtracting with time
Adding and subtracting time is fairly easy and works exactly the same as any other unit; however, we need to always remember that there are only 60 seconds in a minute and 60 minutes in an hour.
Example
A journey starts at 12:35. Give the end time if the journey took 3 hours 45 minutes.
To do this we simply add the two times but making sure to add the hours and minutes separately:
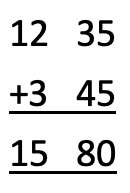
This calculation clearly gives a value for the minutes that is more than 60 and so can be changed to hours plus minutes; 80 minutes equals 1 hour 20 minutes. So the final answer is 16 hours 20 minutes.
Adding times is really only the same as adding any other numbers and the rules for ‘carrying’ numbers apply in the same way. The only difference is that this time we ‘carry’ a number when it is above 60 and not 100.
Example
A man finishes a race at 6.32 pm with a total travel time of 4 hours 57. At what time did he start the race? Here we must subtract times:
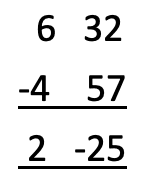
With this example we get a minute’s value of negative 25, which is then taken away from the total hour value, again using the rule of 60 minutes to an hour. This gives an answer of 1 hour 35 minutes.
If you need to brush up on long addition and subtraction and the idea of ‘carrying’ numbers, then we suggest that you do this before completing the exercises in this part of the course.



