In this post
We use energy in different forms every day to provide us with the necessities we need to survive such as warmth and food. We also need energy to generate the electricity we use for a range of devices for entertainment and work and to fuel cars, trains, buses and planes allowing us to travel.
The main use of energy resources is the generation of electricity. The energy we use to generate electricity comes from a range of sources. Some of these sources can be regenerated or used again as their reserves are not running out. These are known as renewable sources and include the Sun, wind and water. However, most of the energy we use still comes from reserves of fossil fuels such as coal, gas and oil. The supplies of these fossil fuels cannot be replenished and are running out. These are known as non-renewable resources.
As technology develops, so does the demand for electricity. As the non-renewable resources are running out and the demand for electricity increases, it is vital that scientists continue to look at the sources of energy we use and develop ways in which we can preserve the supplies of fossil fuels. This may be by using more efficient devices which reduce the amount of energy needed or by researching alternative renewable sources and finding ways to make them more efficient so that the amount of electricity produced by them is greater.
Electricity generation using non-renewable resources
Non-renewable energy resources are those which cannot be recreated or replaced and whose supplies will therefore run out. Examples of non-renewable energy resources include fossil fuels such as coal, gas or oil and nuclear energy sources such as uranium or plutonium. These non-renewable energy resources are used to generate the vast majority of the electricity we use today by providing the initial heat energy required in the generation process.
Fossil fuels
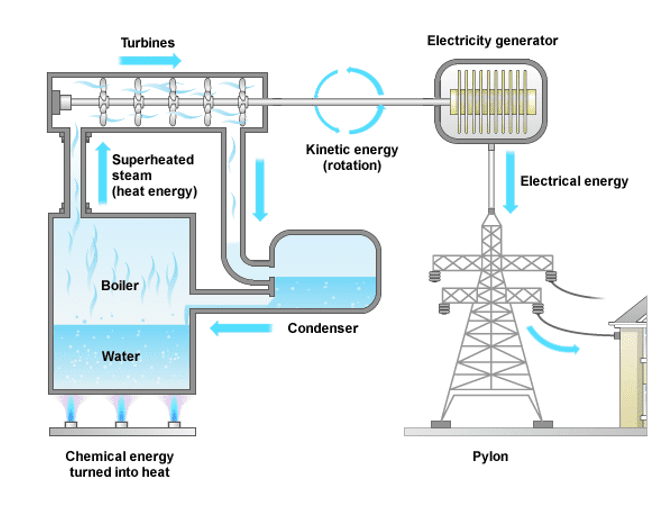
We have been using fossil fuels such as coal, gas and oil to generate electricity for many years, however, the supplies of these are quickly running out. Coal, gas and oil have been formed from the fossils of dead plant life and animals over millions of years. Once they have been used up, they cannot simply be replaced as it would take several millions of years for them to be formed again. Fossil fuels are therefore known as non-renewable energy resources. The generation of electricity using fossil fuels occurs in the following stages
- The fossil fuel is burned in a furnace – fossil fuels contain large amounts of energy in their chemical energy stores. When these fuels are burned, large amounts of this chemical energy are transferred to thermal energy stores. This means that burning fossil fuels produces large amounts of heat energy.
- The large amounts of heat released is used to boil water and make steam – this heat energy is used to heat water in a boiler. The thermal energy is transferred to kinetic energy allowing the water particles to move around through convection. The continual action of the convection current causes the water to boil.
- The steam produced turns the turbine – the steam produced is released from the boiler and the kinetic energy of the gaseous water particles is transferred to the kinetic energy stores of the turbine causing their blades to spin.
- The turbine turns the generator producing an electrical current – the kinetic energy is transferred from turbine to the generator. The generator is a metal core inside an electromagnetic field. As the generator core spins inside the magnetic field, an electrical current is generated. The kinetic energy is transferred to electrical energy.
- The electrical energy generated is then sent away from the power stations and out to the National Grid.
These stages are illustrated using the following diagram:
The use of fossil fuels to generate electricity on a large scale has its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Fossil fuels are reliable and their extraction is relatively quick. This means that any surges in demand can be met by power stations very quickly.
- Fossil fuels are very efficient. A lot of heat energy is produced when they burn. This means that they can supply large amounts of electricity.
- The running costs of fossil fuel power stations are relatively low so they are cost-effective.
Disadvantages
- Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a ‘greenhouse gas’. Infrared radiation emitted from the Sun hits the Earth’s surface and is reflected back. Some of this infrared radiation is reflected back into space and some is absorbed by the layer of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere. This process is essential for life. Without the infrared radiation being absorbed, the Earth would be too cold for life to survive. However, the more CO2 and other greenhouses gases we produce on Earth, the denser the layer of greenhouse gases becomes and the more infrared radiation they absorb. This increase in infrared radiation absorption leads to an effect known as the enhanced greenhouse effect where the Earth becomes warmer and warmer, leading to global warming and the melting of the polar ice caps. There is currently no way of capturing the carbon dioxide but scientists are looking at ways of reducing the emissions.
- Coal and oil may also contain sulphur impurities. When they are burned these sulphur impurities create sulphur dioxide. Sulphur dioxide is an acidic gas which, when released into the atmosphere, combines with water to create acid rain. Acid rain can damage buildings, change the acidity of lakes and rivers, kill wildlife and damage trees and plants.
Power stations now take steps to reduce these sulphur dioxide emissions by coating their chimneys with the base calcium oxide. As the emission gases are passed through the calcium oxide, the sulphur dioxide is neutralised and therefore not emitted out of the chimney into the atmosphere. This costs the power stations more money to maintain which then means that the cost is passed on in the price of electricity.
Nuclear fuel
Radioactive metals such as uranium and plutonium can also be used as nuclear fuels to produce heat energy. This heat energy is then used to heat up water and generate electricity in the same way as discussed previously for the fossil fuels. However, nuclear fuels are not burned to release this heat energy. Instead the uranium or plutonium undergo nuclear fission reactions in the reactor of a nuclear power plant. These fission reactions split the nuclei of the atoms, which release large amounts of heat energy. The energy is stored in the nuclear energy stores of the uranium or plutonium and transferred to heat energy when the process of fission occurs. This heat energy is then transferred to kinetic energy as described previously with the fossil fuel electricity generation.
Nuclear fuels are known as non-renewable fuels because there is a high demand for the specific isotopes needed and once their supplies have been used up, they cannot be replaced.
Advantages
- Nuclear fuels do not produce carbon dioxide or sulphur dioxide emission
- Nuclear fuels produce a large amount of heat energy and are very efficient in electricity generation
Disadvantages
- Nuclear power plants are very expensive to build
- Nuclear fuels are non-renewable
- The use of nuclear fuels generates nuclear waste which is radioactive and hazardous to health. The nuclear waste must therefore be stored safely and securely for thousands of years
- There is a risk of accidents occurring or targeting for terrorism causing spillage of the nuclear waste
Electricity generation using renewable resources
A renewable energy resource is one which is replaceable or can be used again, and will therefore not run out. An example of a renewable energy resource is wood. The same piece of wood cannot be used again. However, it can be replaced by planting a new tree in its place. The disadvantage of using wood to generate electricity is that the burning of the wood creates carbon dioxide, which contributes to the enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming. There are many other renewable energy resources which can be used to generate electricity and which do not produce greenhouses gases.
Water
Generation of electricity using water uses the movement of water from one place to another. The water is not being used up or changed so supplies do not decrease.
One type of power station which uses water are hydroelectric power (HEP) stations.
Moving water has kinetic energy. HEP stations use a dam, behind which a large reservoir of water is allowed to build up. The water is driven up into the reservoir being the dam. The water in the reservoir has gravitational potential energy. The water is allowed to flow down tubes inside the dam which contain turbines. The gravitational potential energy is transferred to kinetic energy as the water flows and mechanical energy as the water is used to turn turbines which are connected to an electrical generator. The generator converts the kinetic energy into electrical energy.
A second way of generating electricity using water involves the use of the movement of waves on the sea and turbines placed in the sea.
As the waves move over the surface of the sea, their kinetic energy is used to turn the turbines. These turbines are connected to electrical generators.
The third type of electricity generation uses tidal barrages. A tidal barrage is a large dam which has been built across the estuary of a river. Tidal barrages rely on the kinetic energy of the water between the river and sea as the tide moves.
The tidal movement of the water produces waves. The kinetic energy of the wave movement causes the turbines in the tidal barrage to spin. These turbines are connected to electrical generators. The kinetic energy is transferred to electrical energy by the generator. The kinetic energy of the tide comes from the movement of the Sun and the Moon causing a gravitational pull on the water.
The advantages of using water as a renewable energy resource include:
- Water supplies are plentiful and are not used up
- No pollution is created
- Minimal running costs
The disadvantages of using water as a renewable energy resource include:
- Large numbers of turbines are needed to generate electricity
- The building of turbines in the sea causes disturbance to the seabed and marine environment which may result in the loss of habitat for some sea creatures
- The turbines will only work when there are waves so they will be unreliable if there is no wind
- Only generate small amounts of electricity so unsuitable for large-scale generation
- There is a limit to the number of suitable places where dams can be built
- The building of dams may also affect the local wildlife and habitats
- Building reservoirs and HEP stations can spoil the landscape and cause loss of habitats
Wind power
Electricity can also be generated using wind power. Wind turbines are used which have large blades mounted on the top of a tower. The tower contains a generator which is connected to the turbines. Wind is caused as a result of convection currents in the Earth’s atmosphere. These convection currents occur because of the heat energy transferred from the Sun.

The wind’s kinetic energy is transferred to mechanical energy forcing the turbines to turn. As the turbines turn, they cause the generator to spin, generating an electrical current. The energy produced by wind energy is very efficient, however, in order for the turbines to turn, the supply of wind needs to be consistent, so the turbines need to be placed in windy areas such as hills or coastlines.
Advantages
- Wind is renewable
- No pollution is created
- No fuel costs
- Can generate large amounts of electricity (depending on the number of turbines)
Disadvantages
- Wind turbines can be noisy
- Wind turbines can spoil the view of the landscape
- Wind turbines cannot be used if the wind stops or if it is too strong
- Wind turbines cannot be used in freezing temperatures
- The power output cannot be controlled or varied according to demand
Solar energy
Solar energy is energy that comes from the Sun. This energy can be used by solar cells to generate electricity or by solar panels as part of solar heating systems to heat up water.
Solar cells
Solar cells are also known as photovoltaic cells. They use the light energy from the Sun to charge batteries and generate small-scale electrical currents. They can be placed on the roofs of houses or in fields to achieve maximum exposure to the light.
The cells convert the light energy absorbed from the Sun directly into electrical energy. Solar cells are only effective as long as there is a sufficient amount of light.

Advantages
- No pollution is generated
- Energy is renewable and free
- Low running costs
Disadvantages
- Cells do not work when there is no light so can only work during the daytime
- The power output cannot be controlled or varied according to demand
Solar panels
Solar panels are placed on the roofs of houses and are used to absorb the infrared radiation emitted by the Sun. Solar panels are part of a solar heating system used to heat up water. The upper panels are made of glass and below the panels are copper pipes which the water supply is pumped through. The copper pipes are coated with a matt black sheath. Dark colours are the best at absorbing infrared radiation so the use of the matt black sheath maximises the absorption of infrared radiation by the pipes and prevents heat loss to the surroundings.
Below the pipes is a layer of thermal insulation with reflective foil on both upper and lower surfaces. This is used to reflect any heat lost back in towards the pipes and minimise heat loss. The heat absorbed by the pipes is used to heat the water. The infrared radiation is absorbed by the black surface and transferred using conduction through the pipes into the water’s thermal energy store.
Advantages
- Solar panels can be used to heat up the water for the house, meaning that there is no need to use gas or electricity to heat your water
- Solar power is renewable and will be there as long as the Sun exists
- No pollution is created
Disadvantages
- The amount of heat energy transferred to the water is dependent upon the amount of infrared radiation absorbed. In cold countries where there is little exposure to the Sun, additional heating methods such as a gas boiler would be needed to heat the water to a high temperature
- Solar panels cannot work in darkness so hot water can only be provided during exposure to the Sun
Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy makes use of thermal energy stores below the surface of the Earth.
Radioactive elements, such as uranium, are found in some types of rocks below the surface of the Earth. These radioactive elements slowly decay and this decaying process creates heat energy. In some areas this heat energy heats surrounding water which then rises up through the rocks and out of the surface of the Earth as hot water or steam. In some areas the water or steam does not rise to the surface so it is necessary to drill down into the rocks, pump cold water down to be heated up by the rocks and returned to the surface as hot water or steam.

This steam can be used to generate electricity. The thermal energy from the rocks is transferred to kinetic energy used to move the steam and then mechanical energy to turn the turbines. The turbines are attached to generators which also turn and the kinetic energy is transferred to electrical energy as an electrical current is generated.
Geothermal energy can also be used to provide underground heating for buildings. Geothermal energy can only really be used in areas of shallow ground where the rocks containing these radiaocative elements are close enough to the surface of the Earth or where it is possible to drill down to them. These areas where the Earth’s crust is thin enough, tend to be in areas where there are volcanoes and volcanic activity.
Advantages
- No pollution is created
- No cost for the energy
Disavantages
- Not many countries have suitable locations for geothermal powerplants
- Not always cost-effective as the cost of builiding the geothermal powerplant can be quite high and the energy it produces can be quite low



