Sir Isaac Newton presented the theory of gravity. This explained the movements of planets and provided an explanation of how the stars and solar system had formed. Newton’s theory suggested that there is a force of attraction between any two objects and this is due to their mass. This is called the ‘gravitational force’. He determined that the size of this force depends on the following factors:
- The masses of the two objects
- The distance between the two masses
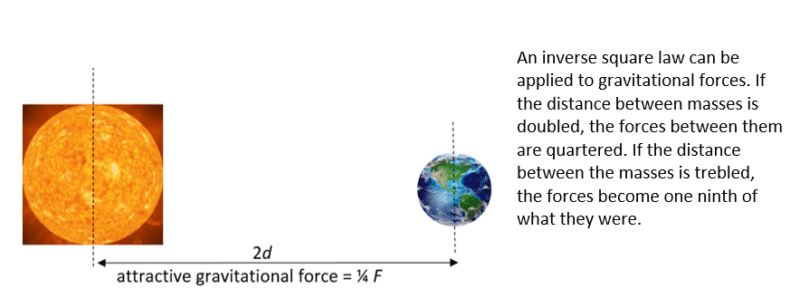
The greater the masses of the two objects, the stronger the force between them. The further away they are from one another, the weaker the forces between them. The diagram below explains this theory.

In the diagram above, the arrows represent the force of gravity. The circles both represent a pair of masses. They are similar in size and are fairly small which means that the law of attraction (gravitational force) between them would be weaker. Sir Isaac Newton compared the acceleration of the Moon to the acceleration of objects on Earth. He believed that gravitational forces were responsible for each and drew the conclusion about the dependence of gravity upon distance.


Interested in a Physics GCSE?
We offer the Edexcel GCSE in Physics through our online campus.









